
Adenomyomatosis & Cholelithiasis Ultrasound Case 183 YouTube
Choledocholithiasis is the most common cause of cholangitis, inflammation and infection of your common bile duct. Backed-up bile causes your bile duct to swell, which further slows the flow of bile. Inflammation and infection can spread from your common bile duct to its branches, including those that run through your liver.

Laparoscopic cholecystectomy for symptomatic cholelithiasis with or without cholangiogram
Cholelithiasis or gallstones are hardened deposits of digestive fluid that can form in your gallbladder. The gallbladder is a small organ located just beneath the liver. The gallbladder holds a digestive fluid known as bile that is released into your small intestine. In the United States, 6% of men and 9% of women have gallstones, most of which are asymptomatic. In patients with asymptomatic.

Complications of Gallstones (Cholelithiasis) Gallstones GrepMed
Cholelithiasis is one of the commonest diseases in gastroenterology. Remarkable improvements in therapeutic modalities for cholelithiasis and its complications are evident. The Japanese Society of Gastroenterology has revised the evidence-based clinical practice guidelines for cholelithiasis. Forty-three clinical questions, for four categories—epidemiology and pathogenesis, diagnosis.

Cholelithiasis/Cholecystitis Stepwards
Gallstones or cholelithiasis are responsible for one of the most prevalent digestive disorders in the United States. They are considered a disease of developed populations but are present around the world. It is both the result of a chronic disease process and the cause of subsequent acute disorders of the pancreatic, biliary, hepatic, and gastrointestinal tract. Over 6.3 million females and.

Complications of Gallstones Cholelithiasis 1. Biliary GrepMed
The goal of this systematic review was to analyze the clinical effectiveness of treatment options for symptomatic cholelithiasis, including surgery, non-surgical therapies, and ED pain management strategies. Methods: Literature search was performed from January 2000 through June 2020, and a narrative analysis was performed as studies were.

Cholelithiasis II Gastroenterology Medicine Animation Medical VLearning YouTube
Symptoms. Gallstones may cause no signs or symptoms. If a gallstone lodges in a duct and causes a blockage, the resulting signs and symptoms may include: Sudden and rapidly intensifying pain in the upper right portion of your abdomen. Sudden and rapidly intensifying pain in the center of your abdomen, just below your breastbone.

PPT Cholelithiasis and it’s Complication PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID2768717
What is choledocholithiasis? Choledocholithiasis, also known as common bile duct stones, refers to an obstruction of the biliary tract caused by gallstones in the common bile duct. The common bile duct is the tube that carries bile from the liver to the small intestine, and it is formed by the union of the common hepatic duct and the cystic duct.

Cholelithiasis, Cholecystitis, and Choledocholithiasis Trial Ex...
Cholelithiasis, or gallstones, are hardened deposits of digestive fluid that form in the gallbladder. The gallbladder is a small, pear-shaped organ that lies beneath the liver and stores bile made by the liver. Bile is a digestive fluid made of cholesterol, bile salts, and bilirubin and gets released into the small intestine through the cystic.

Lowphospholipidassociated cholelithiasis syndrome Prevalence, clinical features, and
INTRODUCTION. Choledocholithiasis refers to the presence of gallstones within the common bile duct. This topic will review the clinical manifestations and diagnosis of choledocholithiasis. The treatment of choledocholithiasis, as well as the epidemiology and the general management of patients with gallstones, are discussed separately:

CholedocholithiasisCausesSymptomsTreatment
Cholelithiasis was selected as one of the target diseases, and the first edition of "Clinical practice guidelines for the treatment of cholelithiasis" was published in 2009, based on a literature search using the Igaku Chuo Zasshi, PubMed, and Cochrane library from 1983 to 2007. Some of the recommendations and statements, however, were.

CholedocholithiasisCausesSymptomsTreatment
In industrialized countries, > 85% of common duct stones are secondary (1 General reference Choledocholithiasis is the presence of stones in bile ducts; the stones can form in the gallbladder or in the ducts themselves. These stones cause biliary colic, biliary obstruction, gallstone. read more ); affected patients have additional stones located in the gallbladder Cholelithiasis.

Cholelithiasis and choledocholithiasis Image
Choledocholithiasis is the presence of stones within the common bile duct (CBD). It is estimated that common bile duct stones are present in anywhere from 1-15% of patients with cholelithiasis. The present-day treatment of bile duct stones is endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP), or in some cases, laparoscopic cholecystectomy with bile duct exploration.
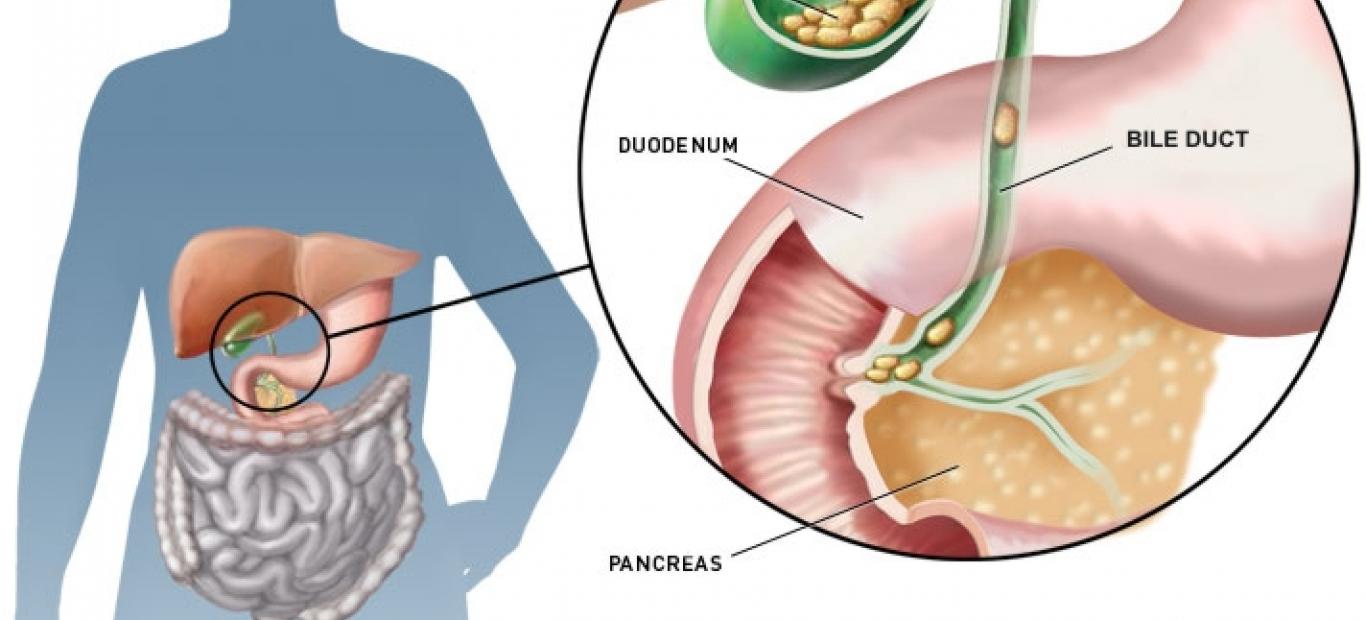
Cholelithiasis Indonesia Re
Cholelithiasis, or gallstones, is one of the most common and costly of all the gastrointestinal diseases. The incidence of gallstones increases with age. At-risk populations include persons with.
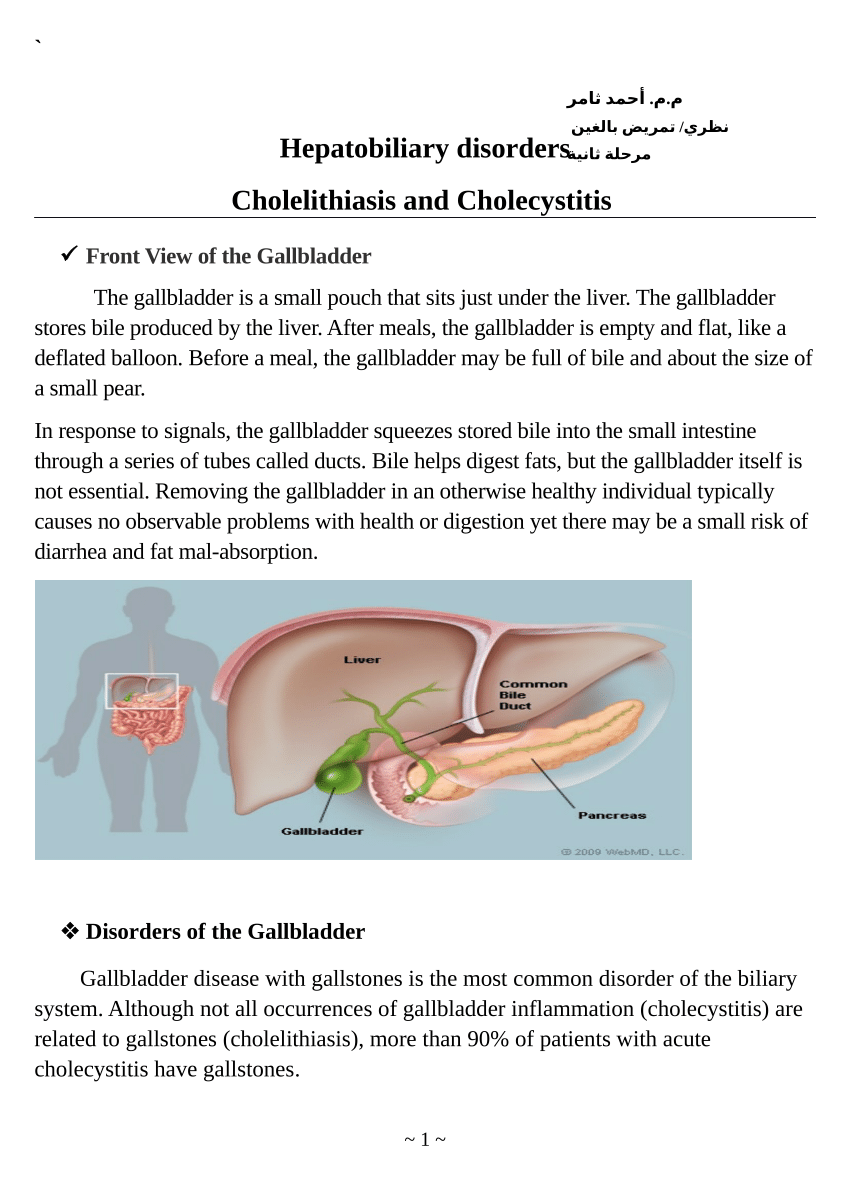
(PDF) Cholelithiasis and Cholecystitis Front View of the Gallbladder
Gallstones can cause upper right abdominal pain. Contact your doctor for persistent symptoms and seek immediate medical care (call 911) for serious symptoms such as severe pain and high fever. The gallbladder stores bile and releases it into the small intestine during digestion. Gallstones can develop if bile contains too much cholesterol or.
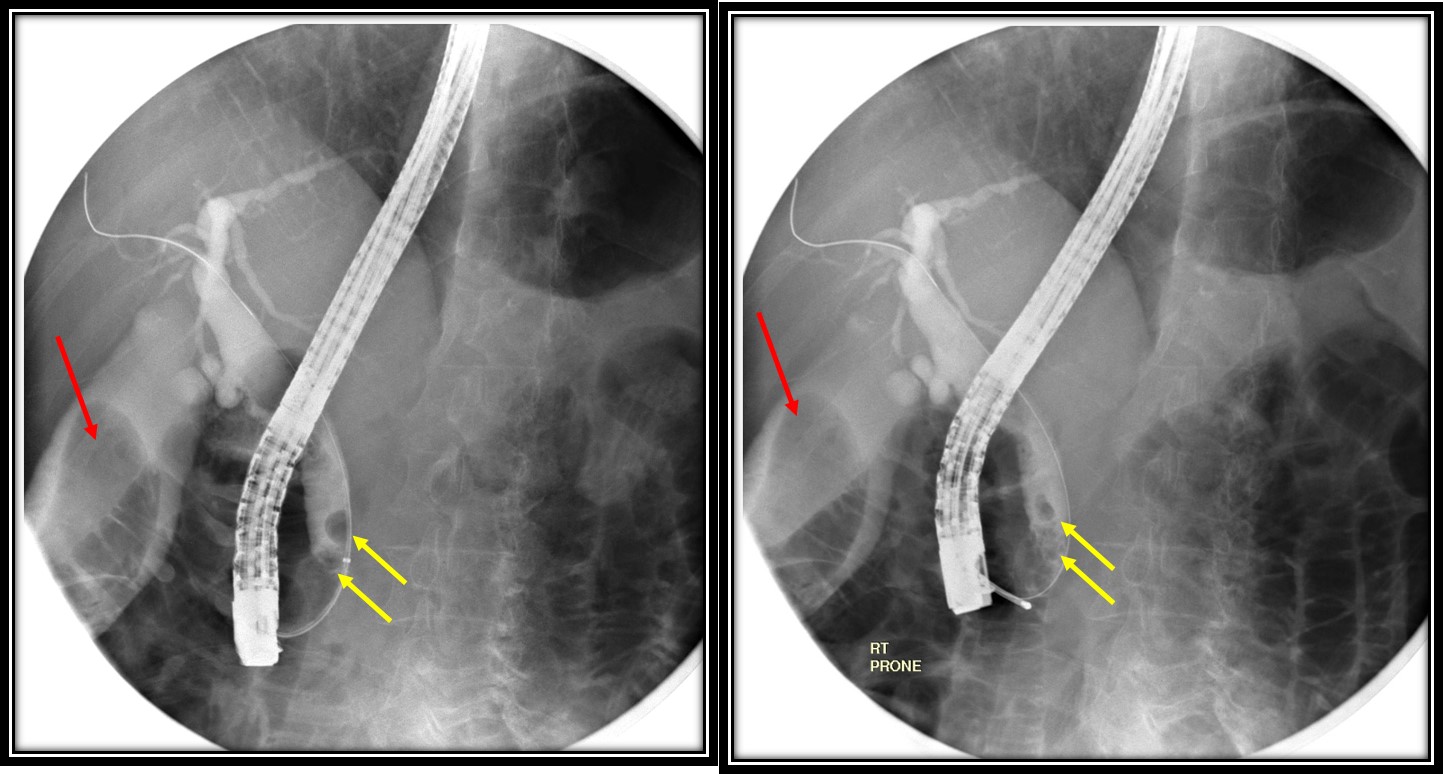
Endoscopic removal of choledocholithiasis Radiology Cases
Gallstones generally don't cause symptoms unless they get stuck and create a blockage. This blockage causes symptoms, most commonly upper abdominal pain and nausea. These may come and go, or they may come and stay. You might develop other symptoms if the blockage is severe or lasts a long time, like: Sweating. Fever.

Choledocholithiasis What Is It, Causes, Diagnosis, Treatment, and More Osmosis
Introduction. Fifteen percent of Americans have gallstones and symptoms occur in up to 10% of patients within 5 years, which can progress to advanced disease such as acute cholecystitis, choledocholithiasis, or gallstone pancreatitis [1-6].Gallstones lead to over one million ambulatory care visits each year, are a leading cause of hospital admissions, and result in one million.