Diagram showing xylem and phloem in plant 7507633 Vector Art at Vecteezy
The xylem is a vascular tissue that transports water throughout a plant's body. The complex processes and various cell types constitute xylem transfer water and dissolved nutrients to maintain and nourish plants. Primary and Secondary Xylem There are two different types of xylem cells based on their origin:
Functions of xylem and phloem Biology Notes for IGCSE 2014
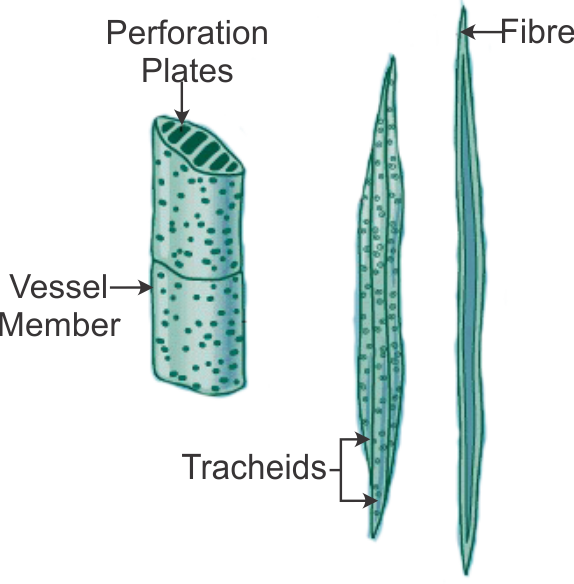
Parts of Xylem The xylem composed of four types of cells. Among these cells, some cells are living and some are dead. The four elements of xylem are: (1). Tracheids (2). Vessels (3). Xylem Fibres (4). Xylem Parenchyma (1). Tracheids Tracheids are the fundamental cell type in the xylem.

The Xylem Tissue Its Structure Function And Importance In Plants
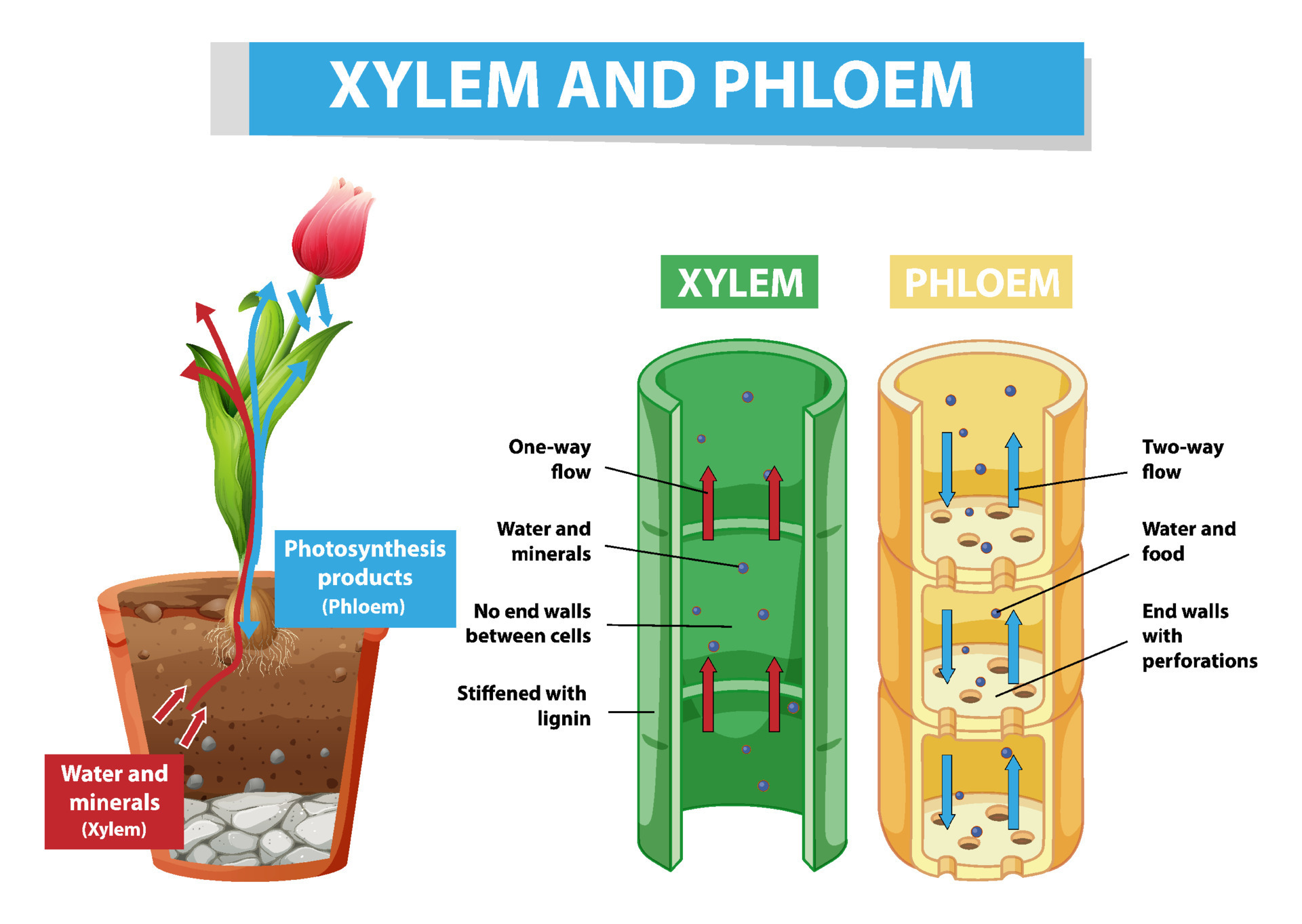
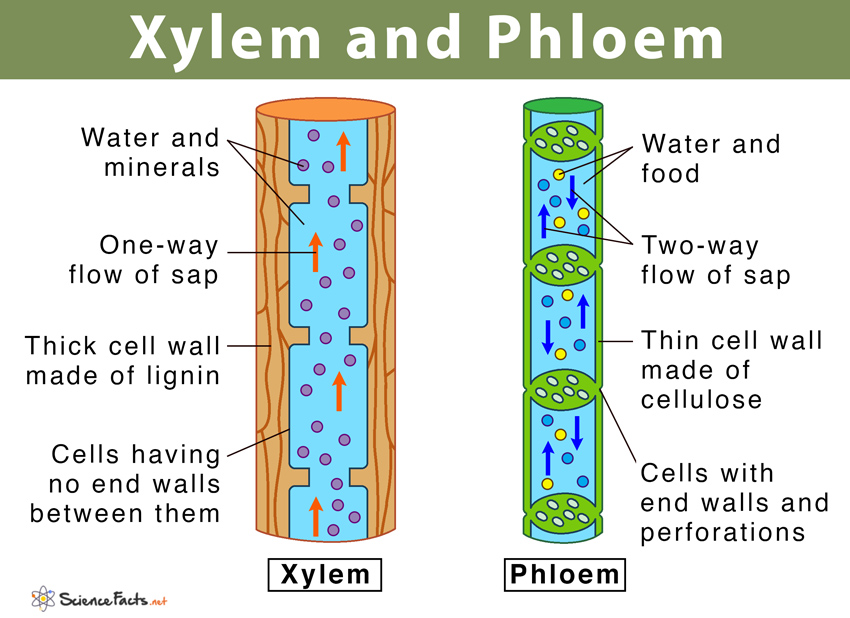
Xylem transports water and mineral salts from the roots up to other parts of the plant. Phloem transports sucrose and amino acids from the leaves and other parts of the plant. Xylem and phloem.

diagram of xylem cells Brainly.in
GCSE OCR Gateway The challenges of size in plants - OCR Gateway Plant transport tissues - xylem and phloem During transpiration plants move water from the roots to their leaves for photosynthesis.
PPT Xylem PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID2419108
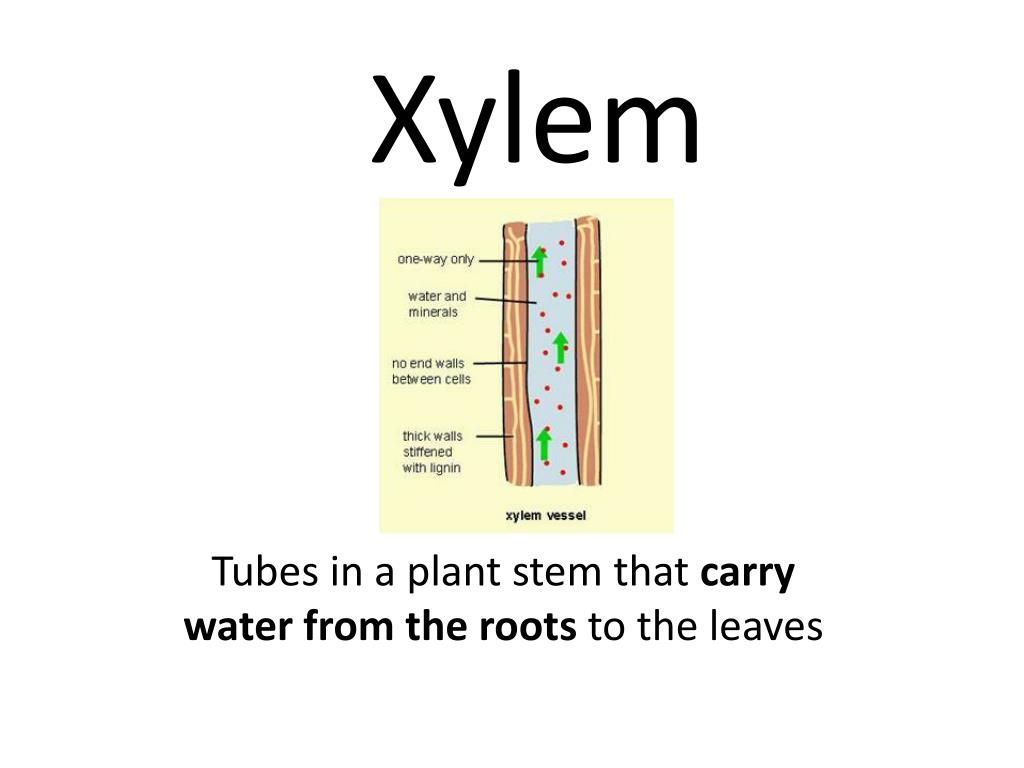
Xylem is the dead, permanent tissue that carries water and minerals from roots to all other parts of the plant. The term 'xylem' is derived from the Greek word 'xylon', meaning wood. Phloem, on the other hand, is the living, permanent tissue that carries food and other organic nutrients from leaves to all other parts of the plant.
9.9 Seedless Vascular Plants Biology LibreTexts
Phloem and xylem are closely associated and are usually found right next to one another. One xylem and one phloem are known as a 'vascular bundle' and most plants have multiple vascular bundles running the length of their leaves, stems, and roots. Xylem tissue is used mostly for transporting water from roots to stems and leaves but also transports other dissolved compounds.

What is a Xylem Cell? (with pictures)
Xylem is a type of tissue in vascular plants that transports water and some nutrients from the roots to the leaves. Phloem is the other type of transport tissue; it transports sucrose and other nutrients throughout the plant.
Draw a labelled diagram of xylem tissues 1n3ed4yy Biology
Xylem: Xylem is a complex tissue forming a part of the vascular bundle. It is primarily instrumental for conduction of water and solutes, and also for mechanical support. Primary xylem originates from the procambium of apical meristem, and secondary xylem from the vascular cambium.

Xylem and Phloem (A Level) — the science sauce
To define Xylem, it is a transport tissue found in vascular plants along with phloem. The important function of xylem is to transport nutrients and water to leaves and stems from roots and also to provide support. The Xylem word was introduced by Carl Nageli in 1858. Now let us see the xylem diagram so that we can have a basic idea of xylem.
Xylem and Phloem Main Differences, Similarities, & Diagram
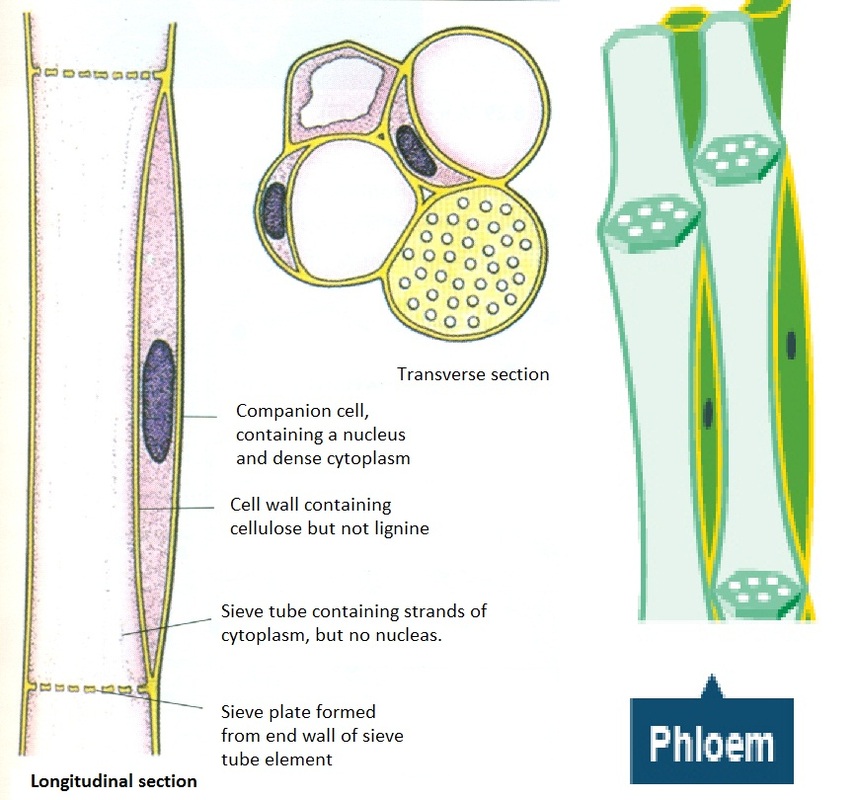
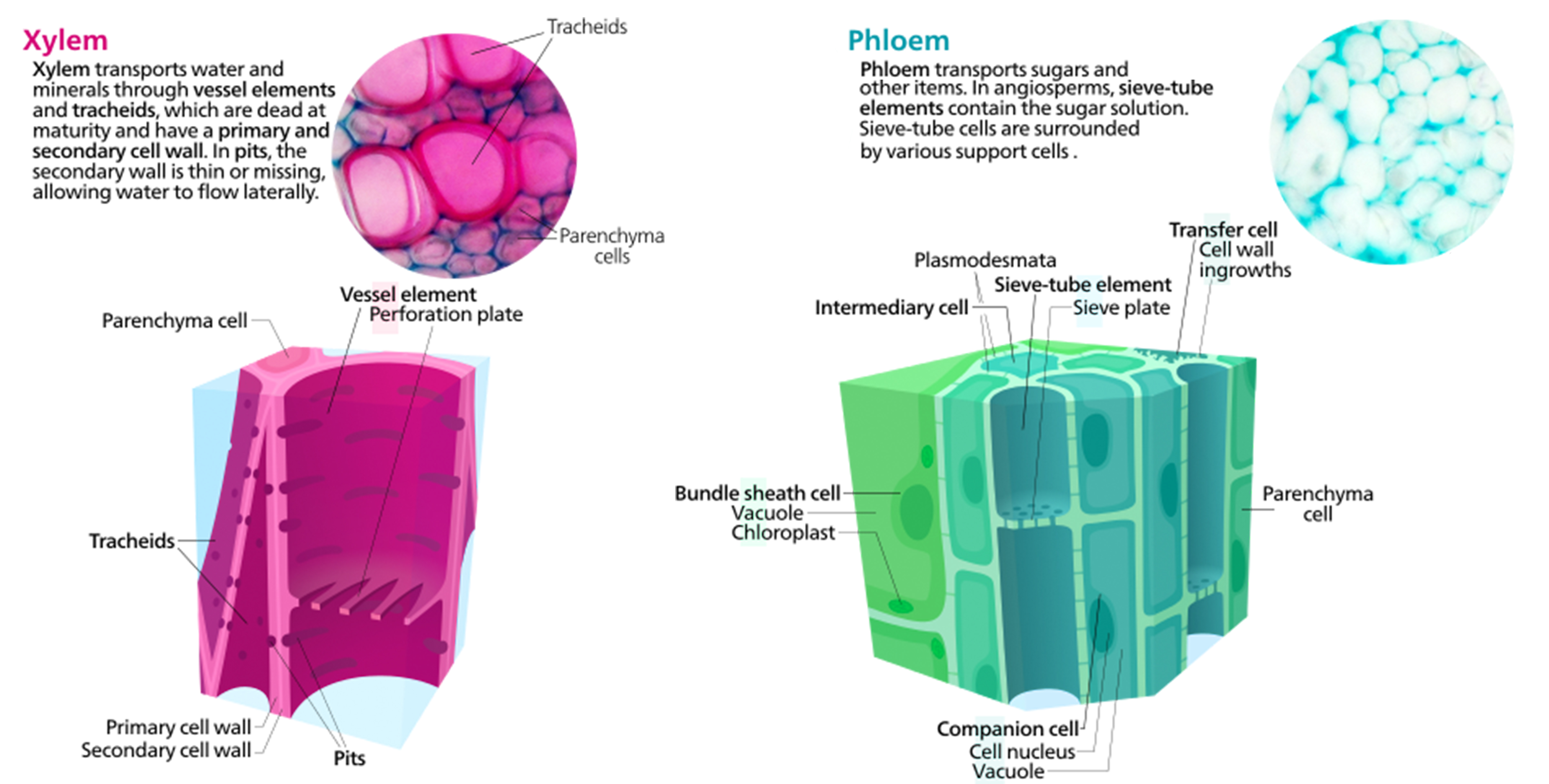
The xylem tissue consists of four main types of cells: tracheids, vessel elements, xylem parenchyma, and xylem fibers. The vessel elements and tracheids are the water-conducting cells. Vessel elements are wider and shorter than tracheids and connect together at the ends. The ends have perforation plates that permit water transfer between cells.
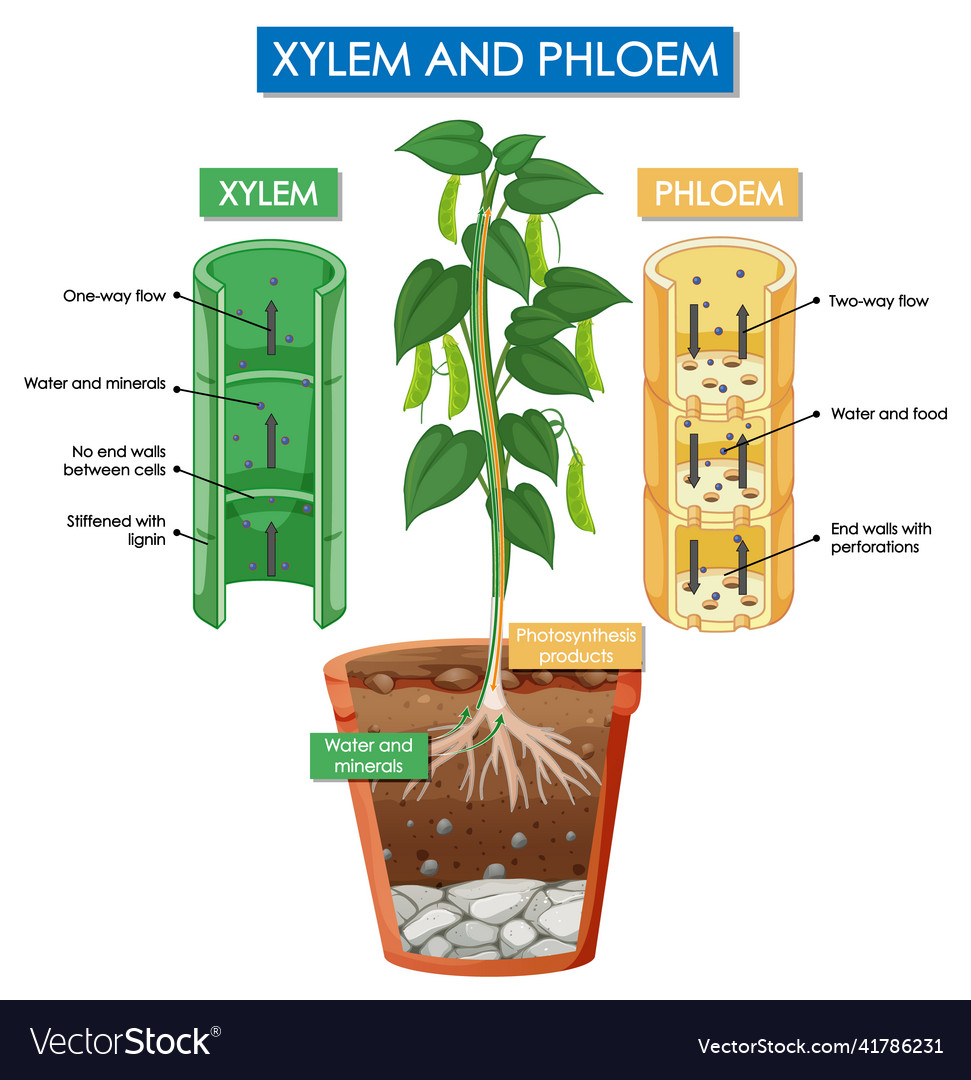
Diagram showing xylem and phloem plant Royalty Free Vector
Xylem tissue has three types of cells: xylem parenchyma, tracheids, and vessel elements. The latter two types conduct water and are dead at maturity. Tracheids are xylem cells with thick secondary cell walls that are lignified. Water moves from one tracheid to another through regions on the side walls known as pits where secondary walls are absent.

Xylem Definition , Structure, Components (Types), Functions And Importance CBSE Class Notes
Together, xylem and phloem tissues form the vascular system of plants. Figure 25.4 B. 1: Xylem and phloem: Xylem and phloem tissue make up the transport cells of stems. The direction of water and sugar transportation through each tissue is shown by the arrows. Xylem is the tissue responsible for supporting the plant as well as for the storage.

Xylem Diagrams
Hello Everyone.Diagram of xylem || How To Draw Xylem Step By Step || Xylem TissueDiagram of Xylem, How To Draw Xylem Step By Step, Xylem Tissue, how to draw.
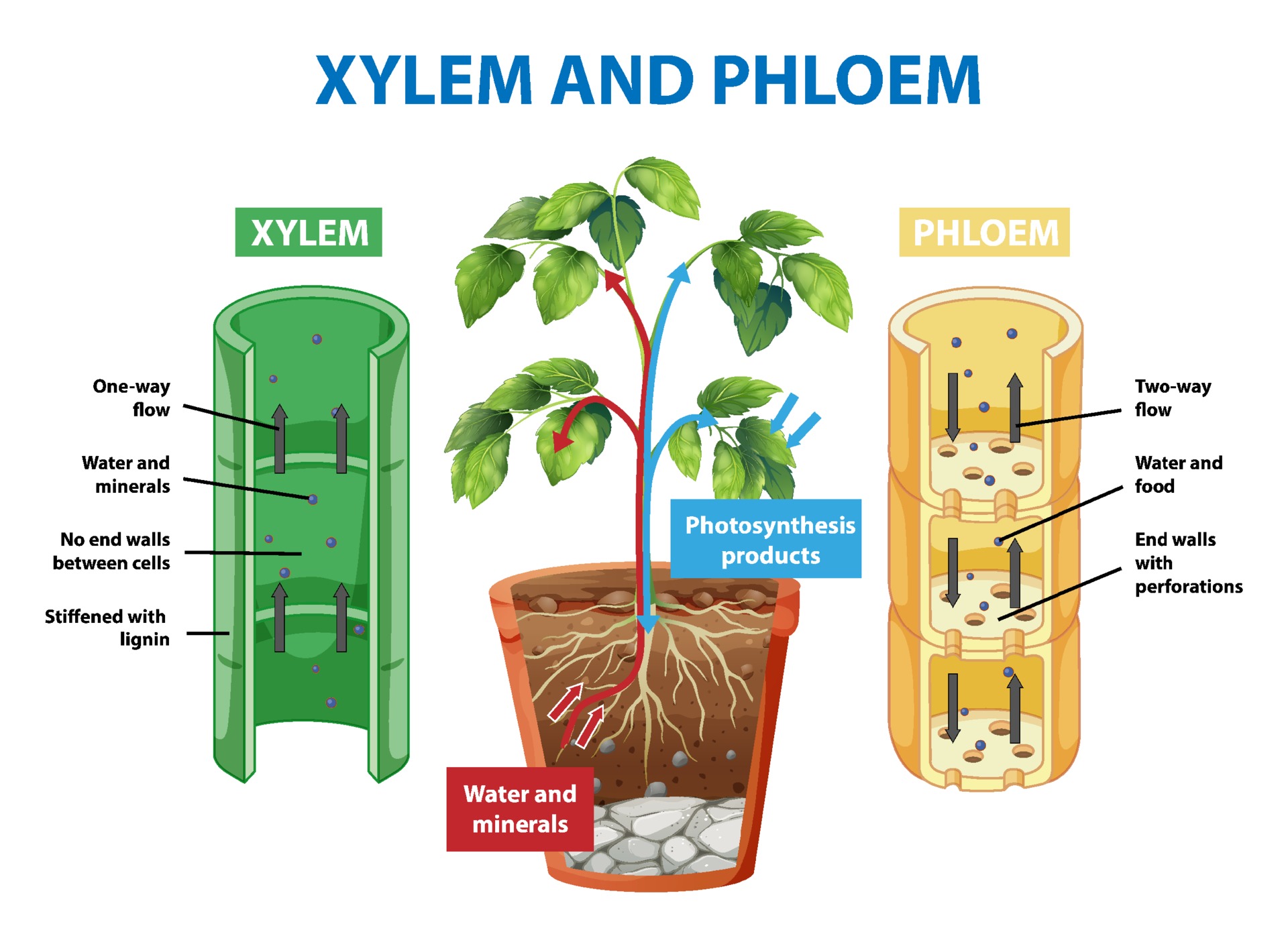
Diagram showing xylem and phloem of plant 1993001 Vector Art at Vecteezy
Together with phloem (tissue that conducts sugars from the leaves to the rest of the plant), xylem is found in all vascular plants, including the seedless club mosses, ferns, horsetails, as well as all angiosperms (flowering plants) and gymnosperms (plants with seeds unenclosed in an ovary). xylem tracheids Tracheid plant cells.

Xylem and phloem water and minerals transportation system outline diagram. Educational labeled
Diagram Characteristics Functions Plant Tissues Plant tissues can be categorised based on their structure and functions performed. 15,86,819 Plant tissues are classified into two types: Meristematic tissues: Cells which perform cell division and are responsible for the growth of the plants.
IGCSE Biology Notes 2.52 Describe the Role of Xylem in Transporting Water and Mineral salts
Diagrammatic structure of xylem cells The most distinctive xylem cells are the long tracheary elements that transport water. Tracheids and vessel elements are distinguished by their shape; vessel elements are shorter, and are connected together into long tubes that are called vessels. [6]