
A Stepbystep Explaination of the Stages of Mitosis
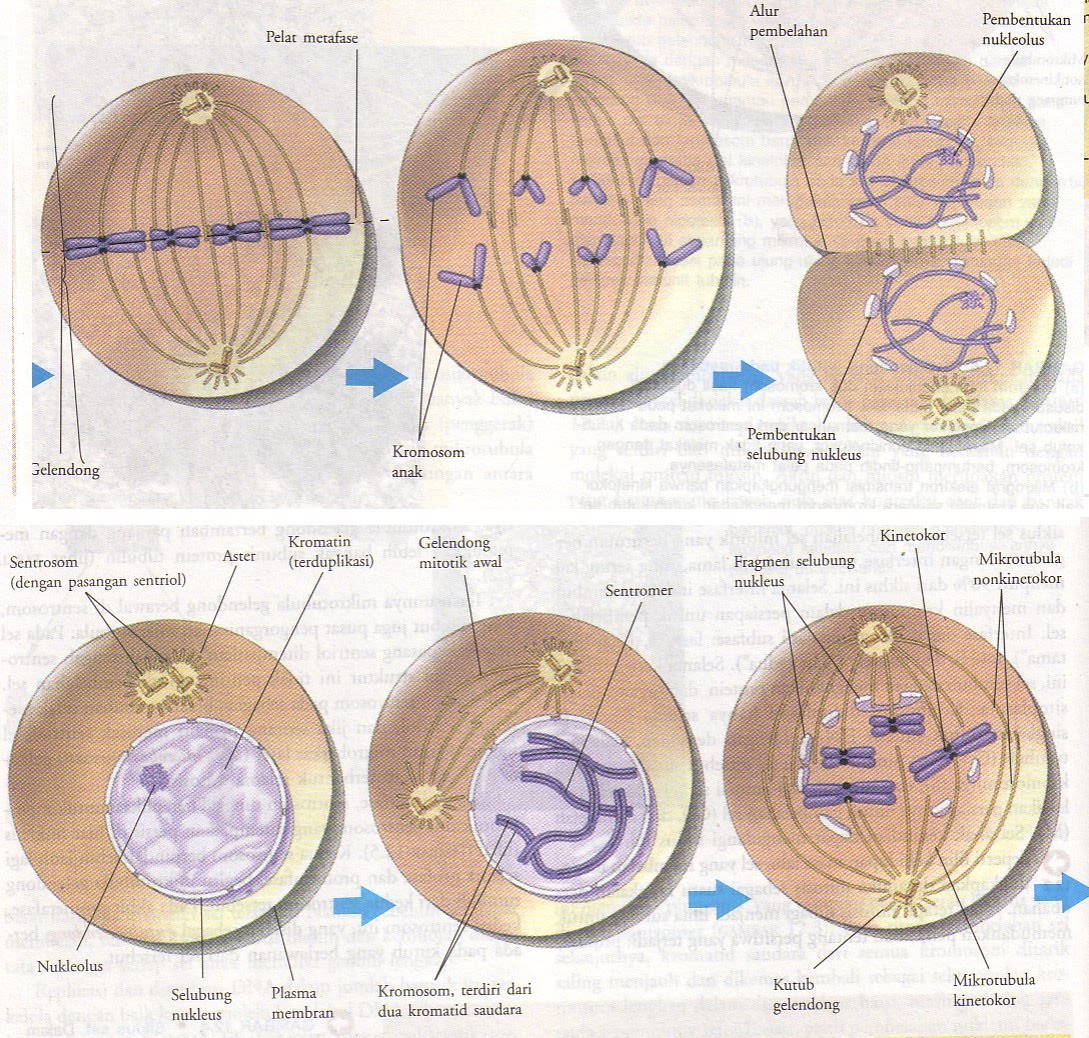
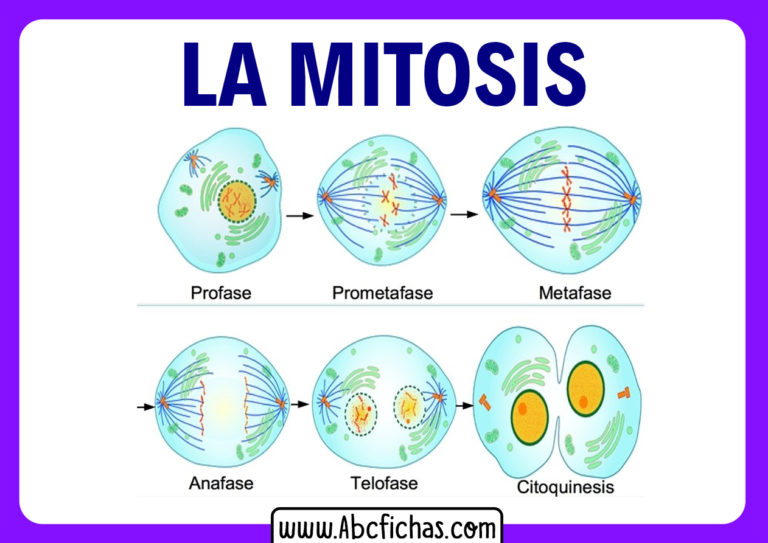
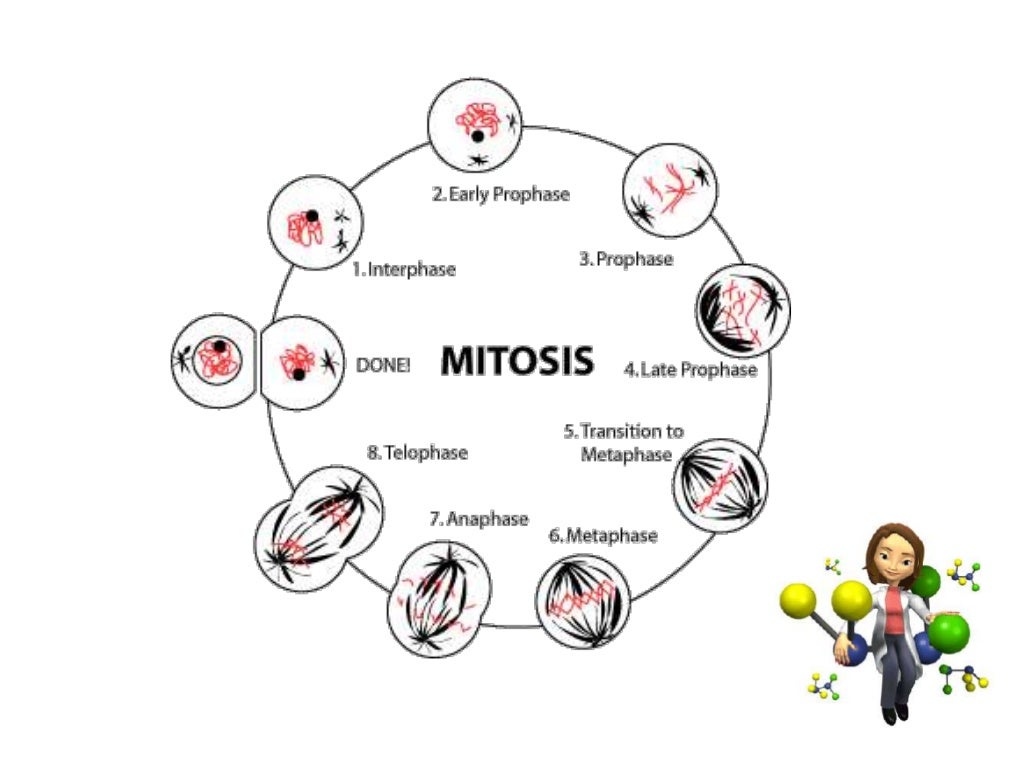
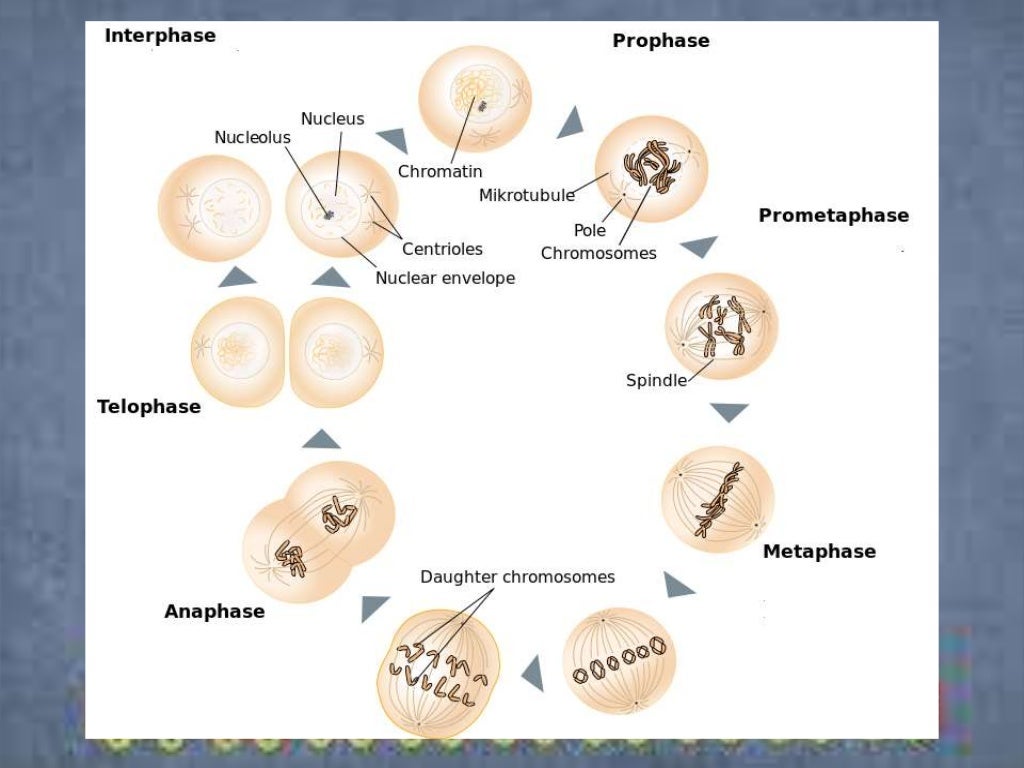
Phases of mitosis. Mitosis consists of four basic phases: prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase. Some textbooks list five, breaking prophase into an early phase (called prophase) and a late phase (called prometaphase). These phases occur in strict sequential order, and cytokinesis - the process of dividing the cell contents to make two.
Gambar Tahapan Pembelahan Mitosis Terbaru
Divide into four phases the reproduction process of chromosomes in plant and animal cells. Mitosis has four stages: prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase. mitosis, a process of cell duplication, or reproduction, during which one cell gives rise to two genetically identical daughter cells. Strictly applied, the term mitosis is used to.
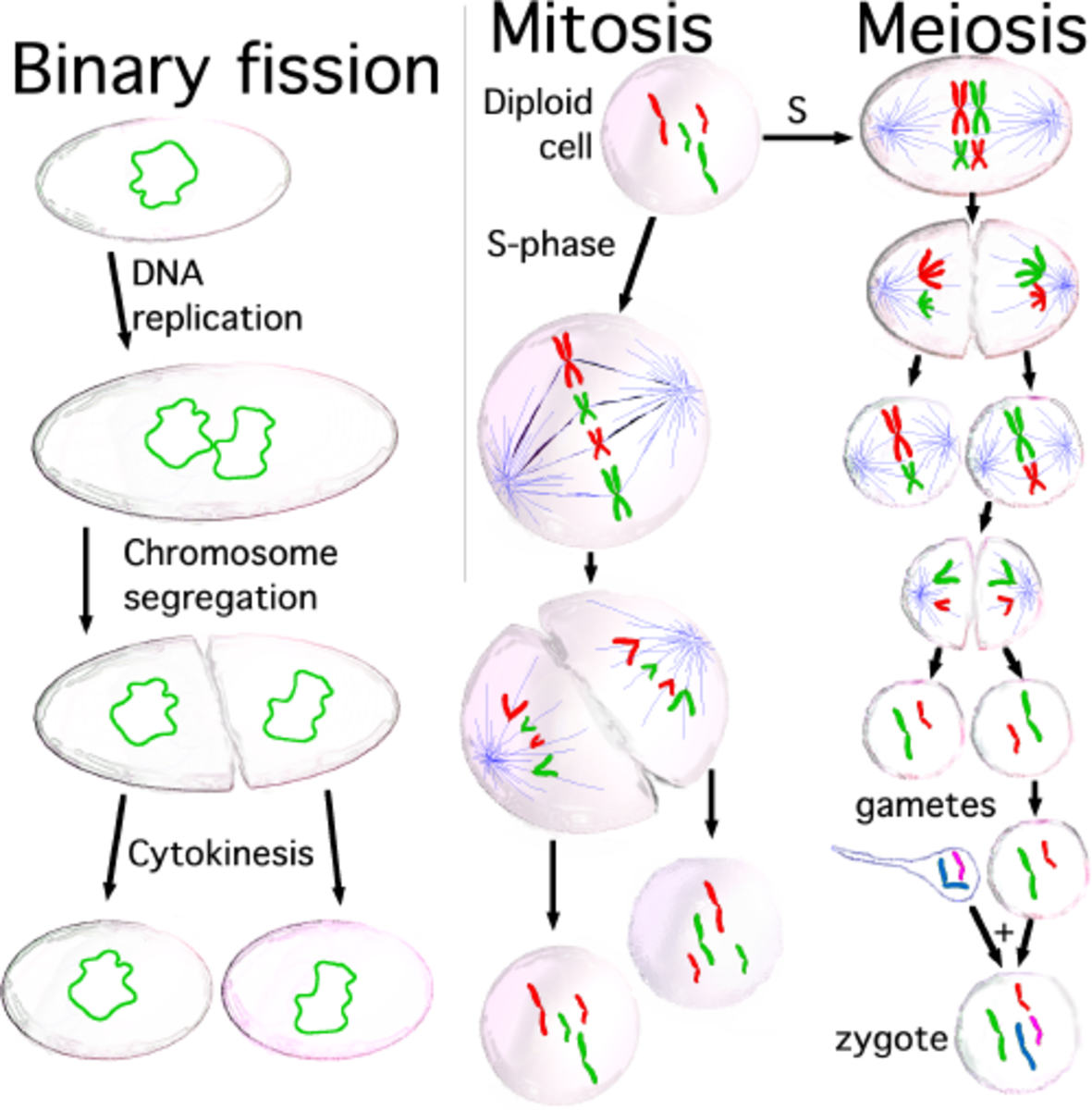
Cell Division Mitosis and Meiosis Owlcation
The mitosis division process has several steps or phases of the cell cycle—interphase, prophase, prometaphase, metaphase, anaphase, telophase, and cytokinesis—to successfully make the new diploid cells. The mitosis cell cycle includes several phases that result in two new diploid daughter cells. Each phase is highlighted here and shown by.
Fases de la mitosis ABC Fichas
Amitosis is a kind of direct cell division in which the parent cell's nuclear and cytoplasmic contents are divided between two daughter cells by a simple cell constriction. It is a type of asexual reproduction among unicellular organisms like algae, bacteria, cyanobacteria, protozoans, and yeasts.

Pembelahan Sel Amitosis, Mitosis, dan Meiosis InformasainsEdu
Amitosis is a widespread form of unbalanced nuclear division whose biomedical and evolutionary significance remain unclear. Traditionally, insights into the genetics of amitosis have been gleaned by assessing the rate of phenotypic assortment. Though powerful, this experimental approach relies on th.

MIOSIS, MITOSIS DAN AMITOSIS Priyo Baliyono
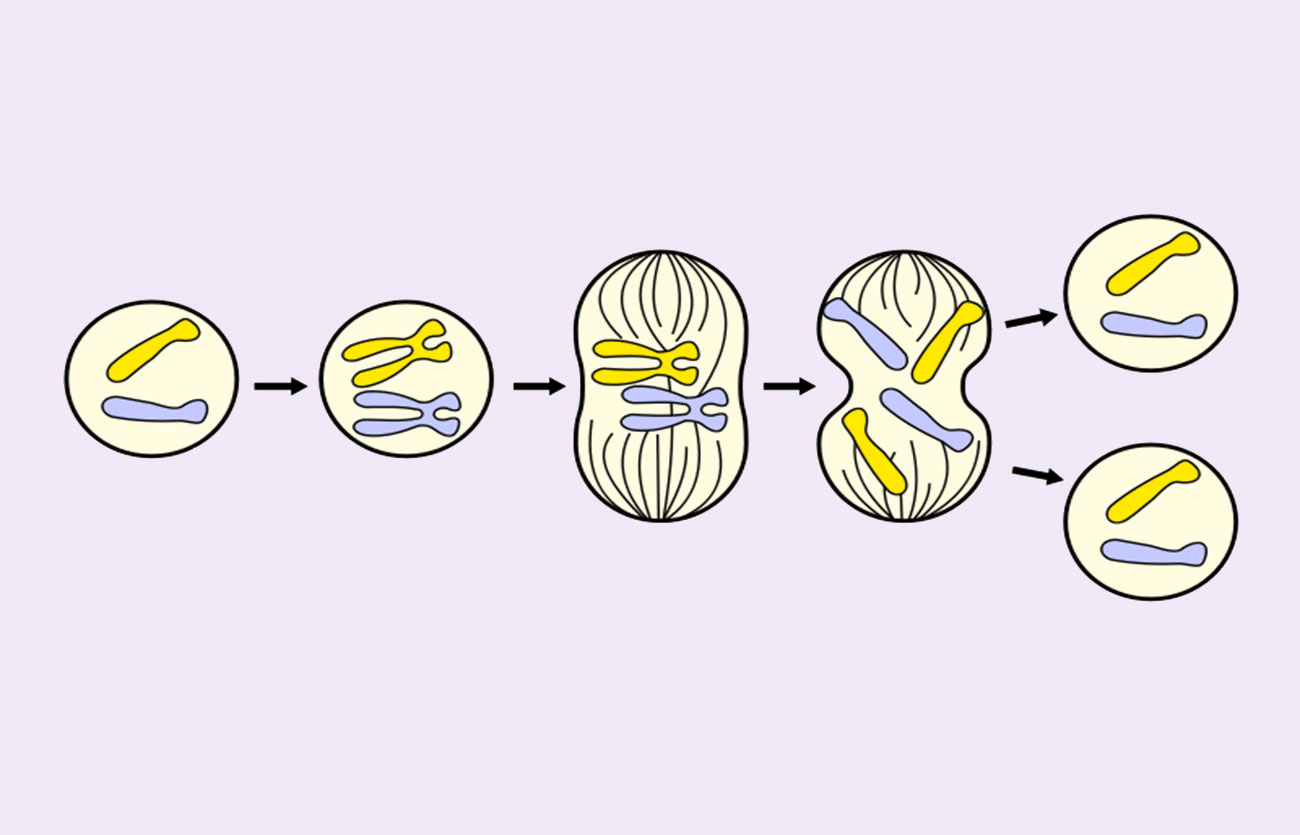
Mitosis divides the chromosomes in a cell nucleus. Label-free live cell imaging of mesenchymal stem cells undergoing mitosis. Onion cells in different phases of the cell cycle enlarged 800 diameters. Mitosis ( / maɪˈtoʊsɪs /) is a part of the cell cycle in which replicated chromosomes are separated into two new nuclei.
Reproduksi sel (amitosis, mitosis, dan meiosis)
LECTURE 1: Mitosis and Meiosis Reading: Ch. 4, p. 83-95; Table 4.2 Book Problems: Ch. 4, # 4-1 - 4-4, 4-7 - 4-10, 4-16 In this lecture we review mitosis, the process by which the chromosomes of somatic cells are apportioned equally to two daughter cells during division. Mitosis ensures that all of our cells inherit the same genetic information.
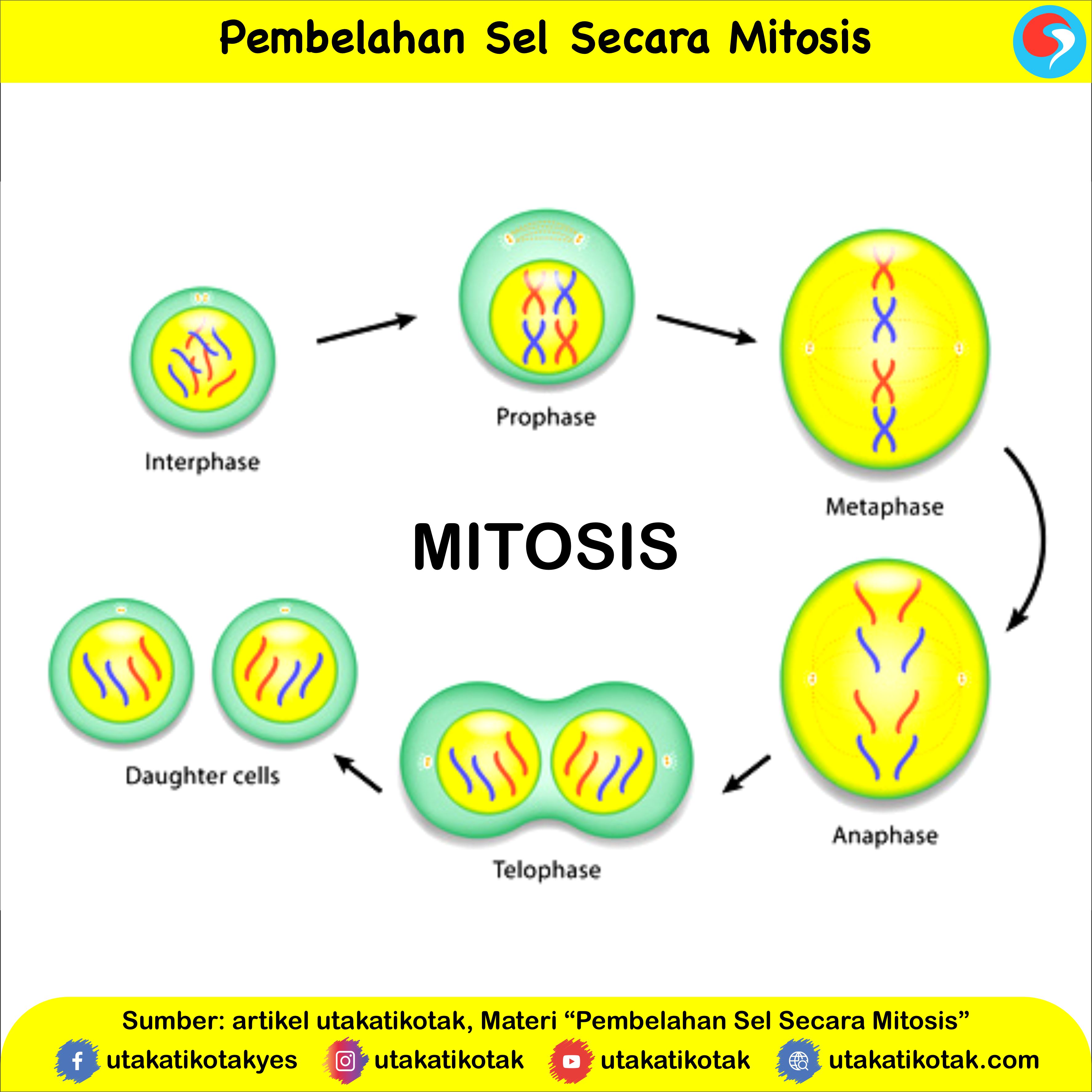
Pembelahan Sel Secara Mitosis
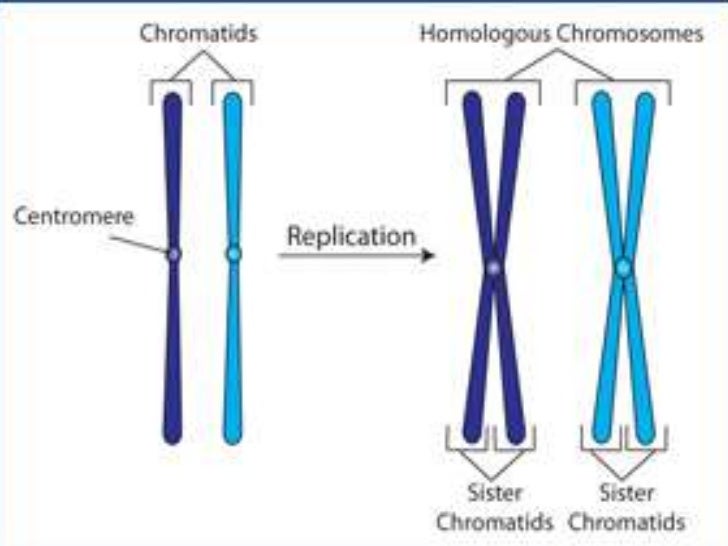
Mitosis. Amitosis. Definition (Oxford Dictionaries) A type of cell division that results in two daughter cells each having the same number and kind of chromosomes as the parent nucleus, typical of ordinary tissue growth. Relating to or denoting the division of a cell nucleus without mitosis. Part of.

Amitosis images, photos et images vectorielles de stock Shutterstock
Amitosis, also called karyostenosis, direct cell division, or binary fission, is a form of asexual cell division that occurs in most prokaryotes. It differs from other forms of cell division (e.g., mitosis , meiosis ) as it does not involve the mitotic apparatus (spindle formation) or the condensation of chromatin into chromosomes prior to.
Diferencias entre mitosis y amitosis Sooluciona
Amitosis is the process of cellular division which majorly takes in the lower organisms like bacteria. This type of cellular division is a primitive type of division in which the nucleus of the cell divides unequally and then the cytoplasm divides. That is, the karyokinesis is followed by cytokinesis. In amitosis the chromatin fibers do not.
Nucleo, amitosis y mitosis
The commonly held view that mitosis and meiosis are the universal forms of cell division is incomplete—some cells can also divide without the intervention of the nuclear spindle following direct nuclear fission, a process known as amitosis. The existence of amitosis has been repeatedly called into question.
senangnya belajar biologi PEMBELAHAN SEL
Firstly, amitosis is a simpler process that occurs in unicellular organisms and specialized cells, while mitosis is a more complex process that occurs in most eukaryotic organisms. Amitosis does not involve the replication of DNA, whereas mitosis ensures the distribution of identical genetic material to daughter cells.
Pembelahan amitosis, mitosis, gametogenesis pada manusia, hewan, dan
During mitosis, spindle assembly ensures fidelity of chromosome segregation into each daughter cell. As such, heterozygous cells remain heterozygous.. Amitosis Gives Rise to New, Functional ISCs, but Can Also Lead to Loss of Heterozygosity (A, E) Schematics of proposed amitosis-driven random homologous chromosome segregation per genotype.
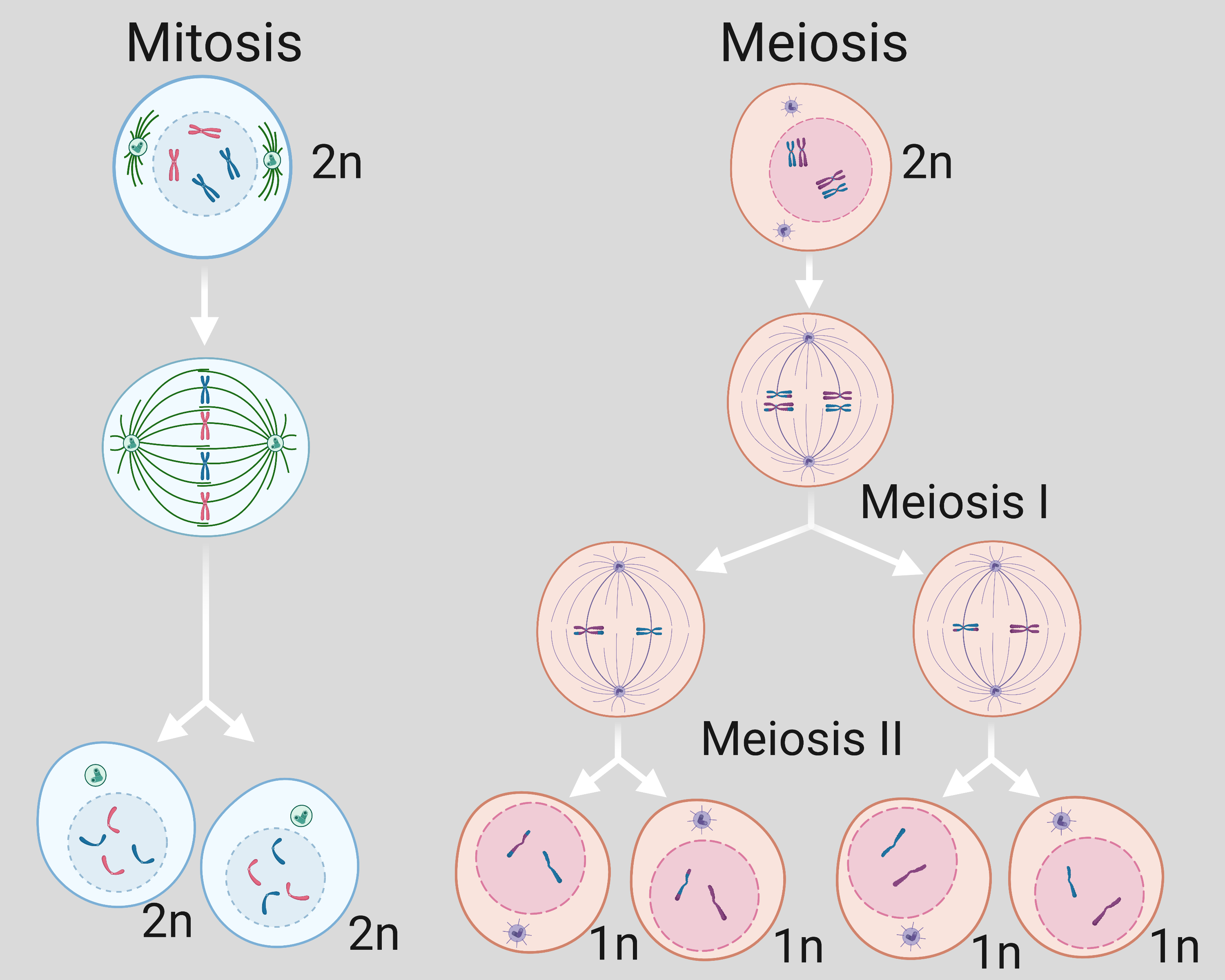
Explain How Mitosis Differs From Meiosis in the Following Ways
amitosis: [noun] cell division by simple cleavage of the nucleus and division of the cytoplasm without spindle formation or appearance of chromosomes.
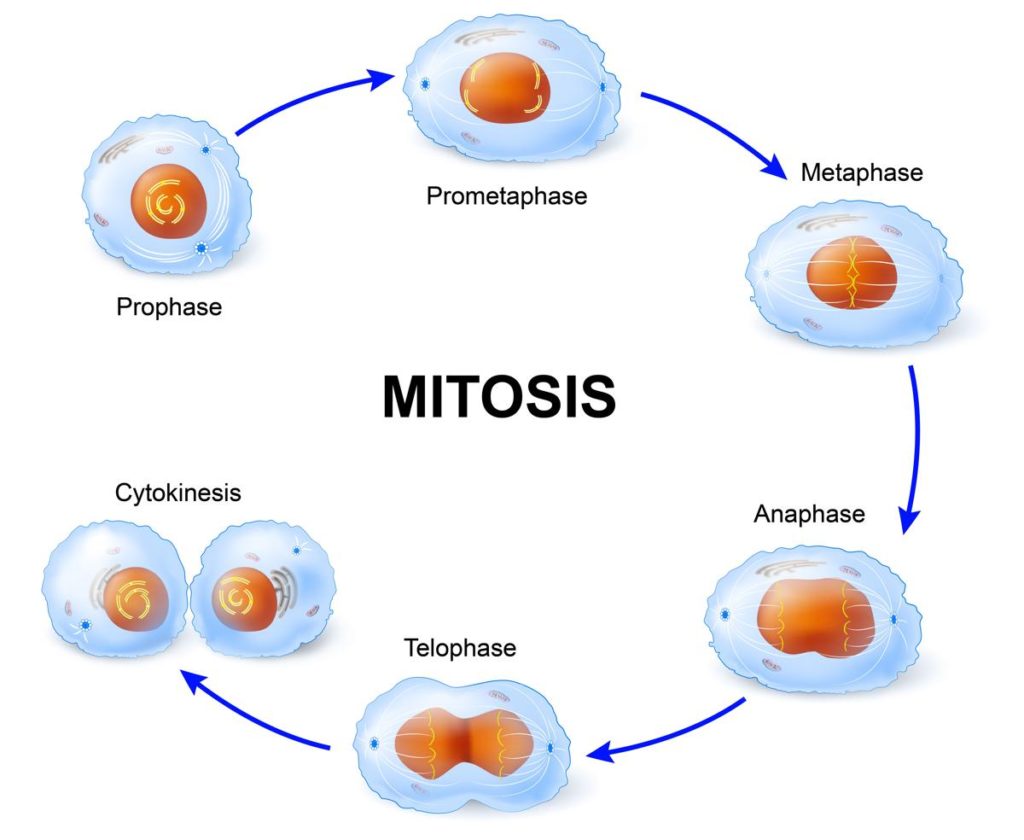
Ejercicio De Pembelahan Sel Mitosis My XXX Hot Girl
Mitosis is a type of cell division that results in two identical daughter cells, each with the same number of chromosomes as the parent cell. Amitosis, on the other hand, is a type of cell division that does not involve the formation of a spindle apparatus and results in daughter cells with unequal distribution of genetic material.

Amitosis dan Mitosis Cell Division
Living organisms need cell divisions to grow or just to stay alive, which can be accomplished in two ways: mitosis and amitosis. The former is characterized by the presence of a spindle structure which pulls apart original and duplicated chromosomes in a cell to ensure the fidelity of daughter cells to its parental one, and the latter is characterized by being devoid of a spindle structure.